The Evolution of AI
AI has evolved dramatically since its inception, moving from early rule-based systems to the sophisticated neural networks used today. The earliest AI systems, developed in the mid-20th century, relied on hand-coded rules to mimic intelligent behavior. However, these systems were limited in their ability to adapt or learn from new information.
With the advent of machine learning and, later, deep learning, AI systems became capable of self-improvement by analyzing data and identifying patterns. Today’s AI models, such as LLMs and image diffusion models, are based on artificial neural networks that loosely mimic the way the human brain processes information. These advancements have not only expanded AI’s capabilities but also raised new ethical and legal questions about how these technologies should interact with society, especially in areas like intellectual property and data privacy.
 Figure 13.
Figure 13.
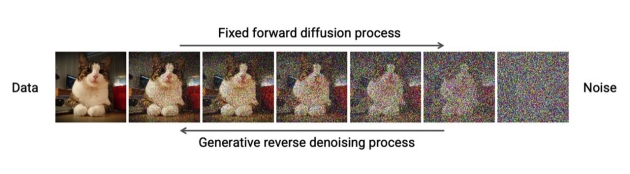 Figure 14.
Figure 14.
 Figure 15.
Figure 15.