AI’s capabilities are rapidly expanding into areas such as video, voice, and image generation. Tools like DeepMind’s WaveNet can generate realistic human voices, while AI-powered video generators are capable of producing entire video sequences from text prompts. These technologies are pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve, enabling entirely new forms of content creation that were previously the domain of human creators.
However, these advancements also raise ethical and legal concerns. For example, AI-generated videos could be used to create deepfakes, which have the potential to cause harm by spreading misinformation. Similarly, AI-generated voices that mimic real individuals raise questions about consent and intellectual property. As these technologies continue to evolve, it will be crucial for legal frameworks to adapt in order to protect individuals' rights while allowing for innovation.
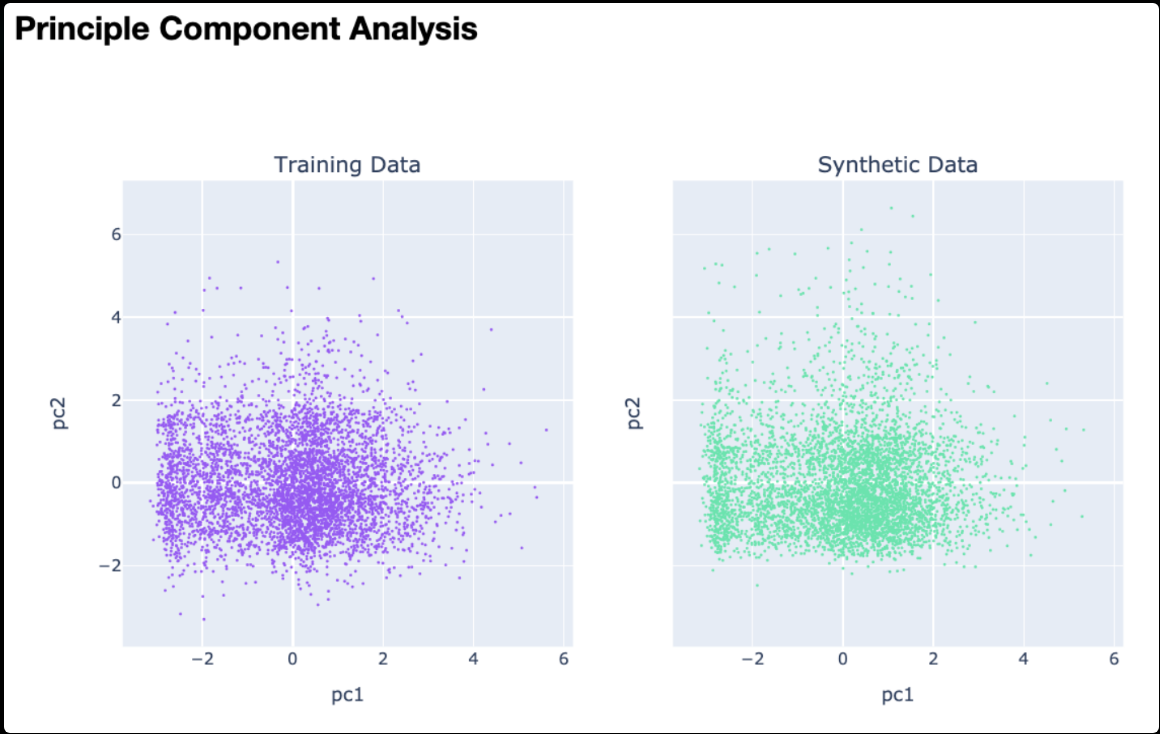 Figure 21.
Figure 21.
 Figure 22.
Figure 22.